The Astria Sequencing Layer
The Astria Sequencing Layer is a decentralized network of nodes that uses CometBFT (formerly Tendermint) as its consensus algorithm. It functions as a blockchain, coming to consensus on an ordered set of transactions. The key feature of this sequencer is that it primarily orders transactions without executing them, as they are intended for execution on rollups. However, it does execute "sequencer native" transactions like token transfers within the sequencer chain.
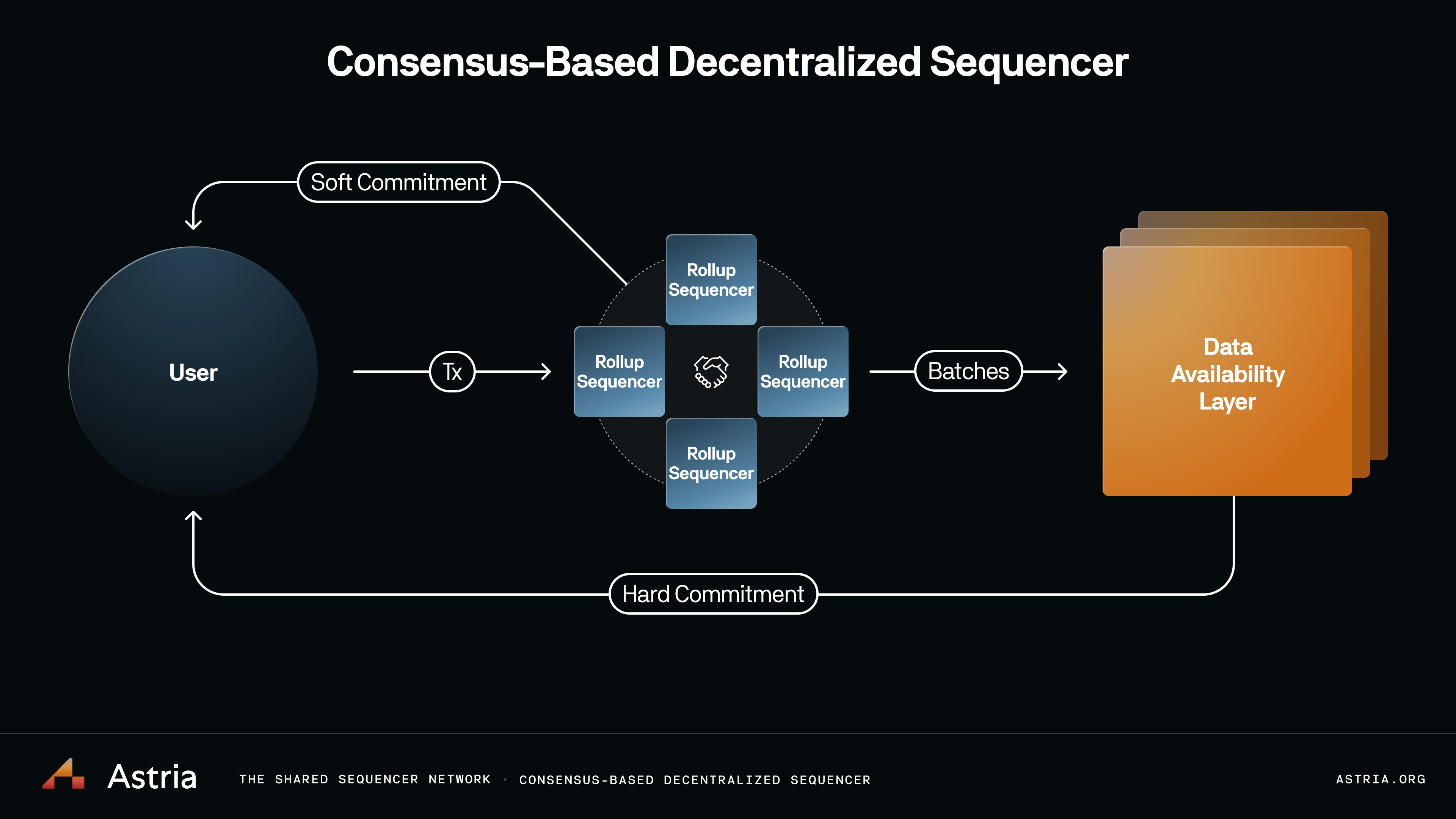
Components of note that are not shown in the above diagram are the Composer, Relayer, and Conductor.
These components facilitate the delivery transactions, batches, and different commits shown above, back to the users.
CometBFT was chosen for several reasons:
- It implements a decentralized leader selection algorithm that rotates between proposers.
- It provides single-slot ("fast") finality, preventing forks and simplifying chain derivation logic for rollups.
- It's battle-tested and widely used in production on many chains.
- It allows blockchain applications implementing ABCI (Application Blockchain Interface) to easily use it as their consensus layer.
- It supports IBC (inter-blockchain communication), enabling potential bridging between many chains.
The Astria sequencer's execution logic is implemented as a CometBFT application in Rust, supporting three main functions:
- Sequencing of rollup data
- Value transfers
- Validator set changes
During consensus, the proposer decides on block transactions and creates commitments to rollup data for each rollup_id. These are verified and finalized if agreed upon by the majority of nodes. This allows rollups to pull only necessary data while verifying its commitment matches what the sequencer chain finalized.
The sequencer network also ensures data availability:
During consensus, block data is made available to all validators for verification and voting on rollup data commitments. After consensus, data is made more widely available via Celestia, a data availability layer supporting data availability sampling via light nodes. Sequencer nodes can optionally act as "validators," actively participating in the production and finalization of new blocks.
This combined approach allows the Astria Sequencing Layer to efficiently order transactions for rollups while maintaining security, finality, and data availability.